The 9th of August, 2015 marked 11 years of the OSM project. On the same weekend Datameet Pune fittingly held its second meetup, ‘Let’s talk Mapping’. The session was led by Devdatta (Dev) Tengshe, a veteran of the Bangalore Datameet group who has several years of experience in GIS and remote sensing having worked previously for ISRO. Dev initiated with a primer on what spatial data is and what can be done with spatial data, then followed with an introduction to GIS, a demonstration of OSM and information on sources for spatial data in the Indian context. His presentation can be found here. Below are the highlights of the session.
What is spatial data? Its uses?
Spatial (data) is not necessarily ‘special’ as many say. It is simply data with a spatial element to it, this could be latitude-longitude but pin codes and postal addresses could be used as spatial formats too. There are numerous advantages to viewing/analyzing social sector data spatially, whether it is census data, land records, city water supply/sewerage networks or other datasets. Spatial representation helps detect patterns and trends that may otherwise go unnoticed. Spatial data in the social sector also comes with its set of challenges. Maps of land parcels for example are not recorded in any standardized way across the country, but instead using local landmarks (turn left at this tree, go straight for 50m, then turn right and head towards the banyan tree) Much of census data is also not easily available at the finer local levels, but only at the district level.
Spatial data can be used to solve spatial problems. Spatial data visualizations work with the strength of the human eye, which is to detect patterns visually. In the exploratory stage you may visualize it to detect patterns, e.g. a map of a user’s Facebook friends may unknowingly reveal areas of low internet penetration, a comparison of Bangalore’s bus routes vs Pune’s bus routes show a stark difference in connectivity. In further analysis you may also find spatial correlations. Spatial modelling is yet another application. These processes are in fact the same ones you would use with regular data, and like all other data, spatial data too requires a lot of cleaning.

GIS 101
The real world is infinitely complex. To represent this spatial world in data we have to develop simplified models. These can be either Vector or Raster models. In vector models, we use points, lines and polygons to represent real world features (e.g. bus stops, bus routes, ward boundaries) whereas in raster models we use images of the earth’s surface taken by satellites, or UAVs which are composed of pixels to view the earth’s surface.
File formats for spatial data:
Vector
shapefiles are used within desktop softwares (QGIS, ArcGIS), geojson is used for web mapping (these are light, human and machine readable), kml (first developed by Keyhole, later bought by Google) is also a common format.
Raster
tiff (multiple bands) format allows for storage of larger datasets.
Spatial databases are now able to handle spatial data, allows spatial queries related to it, so a user doesn’t have to write out the logic for such operations (e.g. of spatial queries: Find the nearest school/hospital to this village?). Spatial databases are used by retail businesses, housing, utilities and many other commercial ventures.
Where do I get spatial data?
The Beg-Borrow-Steal theory
Beg
Create it yourself. In the process of field work you can use field kits to collect spatial data for your area of interest. Tools available for this include Locus map free – Outdoor GPS (App) OR Open Data Kit (Software suite). As an alternative, you may also digitize from satellite maps
Borrow and convert it
Data that may be available freely but not in a form that is easily usable and may need to be georeferenced.
“Steal”
Spatial data can be ‘scraped’ from websites that contain this data but do not make it easily available, see github datameet maps for examples of data collected from census websites. Although permission may not explicitly be given for this, since it is already up on the web and no copyright exists on the data it is implicitly understood to be open source.
Open Street Map (OSM)
The Wikipedia for spatial data, OSM, counts more than two million users who voluntarily contribute to the project. OSM was first aimed to collect just street data, but it has now expanded tremendously. City data in OSM is of high quality however for rural areas, only major roads can be guaranteed.
Unlike Google maps which does not allow a user direct access to its data, OSM raw data is available for download as well as editing. Within OSM users can tag different aspects of any object, giving others more information about it. Users can also introduce new key:value pairs if needed. OSM scripts monitor changes and an IRC chat room verifies these changes. OSM updates frequently and is therefore used in humanitarian situations (HOT OSM). Only 12 servers run all of OSM
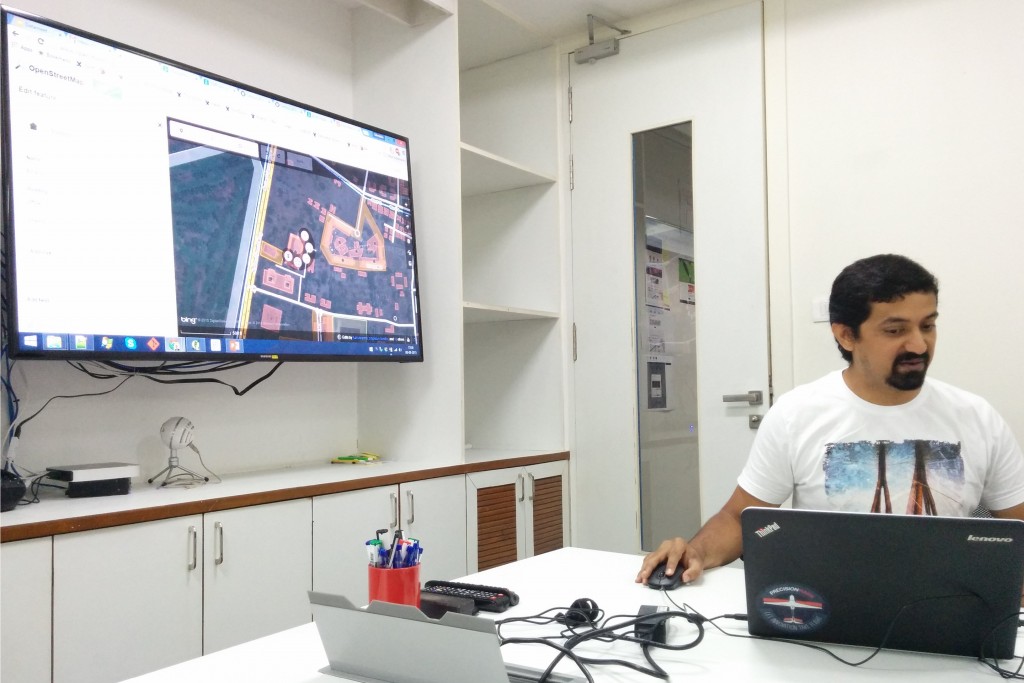

Wikimapia in comparison is limited, it allows you to draw on google maps, but there is no verification of additions and limited data download.
There are independent initiatives to make available raw data download from OSM [See slide 47] Similarly other apps use and make available OSM data, Map quest for instance gives directions based on OSM data. If you are unsure of the final use of your data you can download data in OSM XML format, since it contains everything. GeoJSON is useful only when you need shapes, not other features of spatial data.
Sources
- Downloading OSM data for a country: Geofabrik
- Downloading OSM data for any custom polygon: BBBike
- Raw data based on particular data queries: Overpass Turbo
Spatial data in the Indian context
Districts/Tehsils
Shapefiles for districts and tehsils are available on Github, Datameet maps. However maps must be verified against other sources of data. In reality there is dispute even within the Indian government on how many districts India has.
Village boundaries
In reality, in many cases no fixed village boundaries exist, the Census uses blocks and settlements for reference. Some states however make available static maps showing village boundaries that can be georeferenced.
Pin codes
Can we divide the country into pin codes? Pin codes do not represent an area, they are points along a line where the postman will deliver. Hence the assignment of addresses to the last three digits of a pin code is a decentralized decision. The lowest level of post offices decides. Pin codes also do not cover the entire country. Post offices to Pin codes do not have a one-to-one relation.
Census data
Census data at the finest spatial level comes down to census ward boundaries. Nobody outside the census department actually knows these boundaries. Pune city has 700 census ward boundaries (which do not correspond to administrative/electoral ward boundaries) mostly hand drawn. District level offices may have maps with these boundaries as hard copies.
Nothing in national policy disallows them from sharing them, but nevertheless government officials aren’t inclined to share such information. Certain limitations however do exist on government data sharing, protected military areas, areas near the national boundaries, topography maps etc. are prohibited.
Basemaps and DEMs (Digital Elevation Models)
The Open data initiative of the Government of India has created some 5400 odd ‘Open Series maps’ i.e. toposheets without height information. None of these are done digitally or printed. They can however be used with gps data since the lat-long is accurate.
Since GoI topography data isn’t made openly available, alternatives available are SRTM, ESTER and Bhuvan Cartosat. These are good for example for larger rural areas, but not feasible for urban areas. Private companies work with UAVs for very high resolution elevation data. For satellite imagery as basemaps, Landsat imagery, going back to 1970 is available.
Closing Remarks
In following up with our discussions on mapping, for those of you who are interested, we have several Pune specific mapping tasks that individuals can contribute to. E-mail us at pune@datameet.org for more information. We hope that everyone found the discussion useful and thank you for coming, thanks to Dev for the informative session! Thanks to Shraddha and Thoughtworks Pune for hosting us. Do connect with us via social media [Twitter] or join our mailing list for information on the next meeting.


 nday
nday  and comparable data, such as the
and comparable data, such as the